Chromatic confocal sensor, also called confocal displacement sensor or confocal distance sensor, is a high precision measuring instrument/device. It's working principle is that chromatic lights with different wavelengths can be used for measuring various kinds of data of objects, such as displacement, distance, thickness, height, depth, flatness, roughness, profile, radius, porosity, vibration, etc. This technology is used in industrial field most.
Before we dive into the details of its working principle, let's have a learning on white light first.
White light is a kind of natural light which is composed of seven colors: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. In 1666, Newton studied sunlight with a prism and concluded that white light is made up of a mixture of different colors with different wavelengths. White light can be refracted through a prism into seven color bands: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.
Chromatic confocal sensors use this principle to disperse white light into a variety of color light, and detect the wavelength of reflecting light to get a variety of data of the objects such as displacement, thickness, flatness, etc.
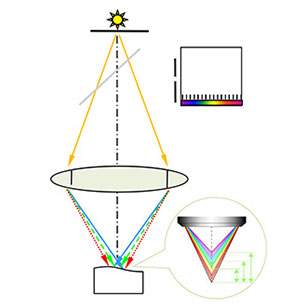
A beam of white light will be dispersed into different chromatic lights with different wavelengths after passing through a hole and a lens. These lights will focus on different positions of the optical axis. All lights irradiated on the surface of the object will reflect back.
All reflecting lights will reach a spectroscopic component. The lights, which are not irradiated on the intersection point of the optical axis and the surface of the object, will be led to the periphery of the hole of the spectrum analyzer. They will not interfere with the measurement.
Only the light irradiated on the intersection point of the optical axis and the surface of the object can enter the spectrum analyzer. The displacement from the sensor to the object will be figured out through analyzing the wavelength. Combined with software, various kinds of data of the object can be figured out.